In-Depth Analysis of 3D Printing and Related Technologies
-Exploring the Diverse Facets of 3D Printing from Rapid Prototyping to Additive Manufacturing
3D printing, as a key technology in the material industry, has demonstrated its unique value and potential applications across various domains. This technology not only allows for the creation of three-dimensional objects based on digital models but also provides innovative solutions in medical, aerospace, construction, and many other industries. Here are some terms closely related to 3D printing, along with their similarities and differences:
1. Rapid Prototyping (RP): Rapid prototyping is a technique that uses digital model files to quickly fabricate a prototype or part through a layer-by-layer accumulation process. Its similarity to 3D printing lies in the layer-by-layer object creation method. However, rapid prototyping emphasizes speed and efficiency, primarily used in the product design phase for quick evaluation and modification of designs.
2. Additive Manufacturing (AM): Additive manufacturing is a broader term that encompasses 3D printing, referring to any process that creates objects by adding material layer by layer. Compared to 3D printing, additive manufacturing highlights the industrial application of the manufacturing process, including production activities with various materials such as metals and plastics. Additive manufacturing is used not only for prototyping but also for the manufacturing of final products.
3. 3D Rapid Prototyping: This term refers to the application of rapid prototyping techniques in the 3D printing field, emphasizing the use of 3D printing technology to quickly create product prototypes. It combines the speed and efficiency of rapid prototyping with the technological advantages of 3D printing, making the process from concept to physical object faster and more precise.
Although these terms and technologies overlap in certain aspects, they each focus on different highlights and application areas. 3D printing, as a widely used term, covers applications ranging from personal to industrial levels, while rapid prototyping and additive manufacturing are more often applied in product development and manufacturing, especially when seeking speed, efficiency, and material diversity. Understanding the subtle differences between these terms can help accurately grasp the development dynamics and application scope of 3D printing technology and its related fields.
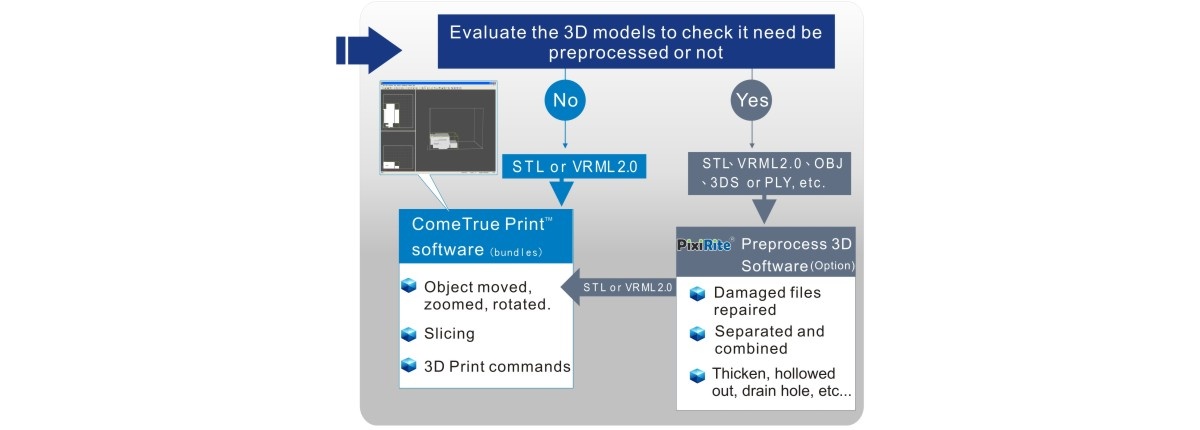
ComeTrueⓇ is especially renowned for its innovation in the 3D printing technology domain, capable of creating colorful models and printing ceramic materials. This offers a wide range of possibilities for educational tools, artistic creation, and professional prototypes. The diversity of these brands and technologies showcases the extensive application and significance of Binder Jetting technology in modern manufacturing, design, and educational domains. https://www.cometrue3d.com/en/ac/cometrue%C2%AE-binder-jetting-cbj
